 Politics
Politics






A. Merkel
Europe is a mosaic of cultures that makes our continent so unique.


D. Kennedy
Europe is where history meets modernity and tradition meets innovation.


J. Delor
Europe is history and civilization and culture and ideas and dreams. It is the future and the hope of all our peoples.


D. Berbatov
Europe is the symphony of differences combined with convergence of values.

More about civic education in our lives - EUROPE
 Politics
Politics
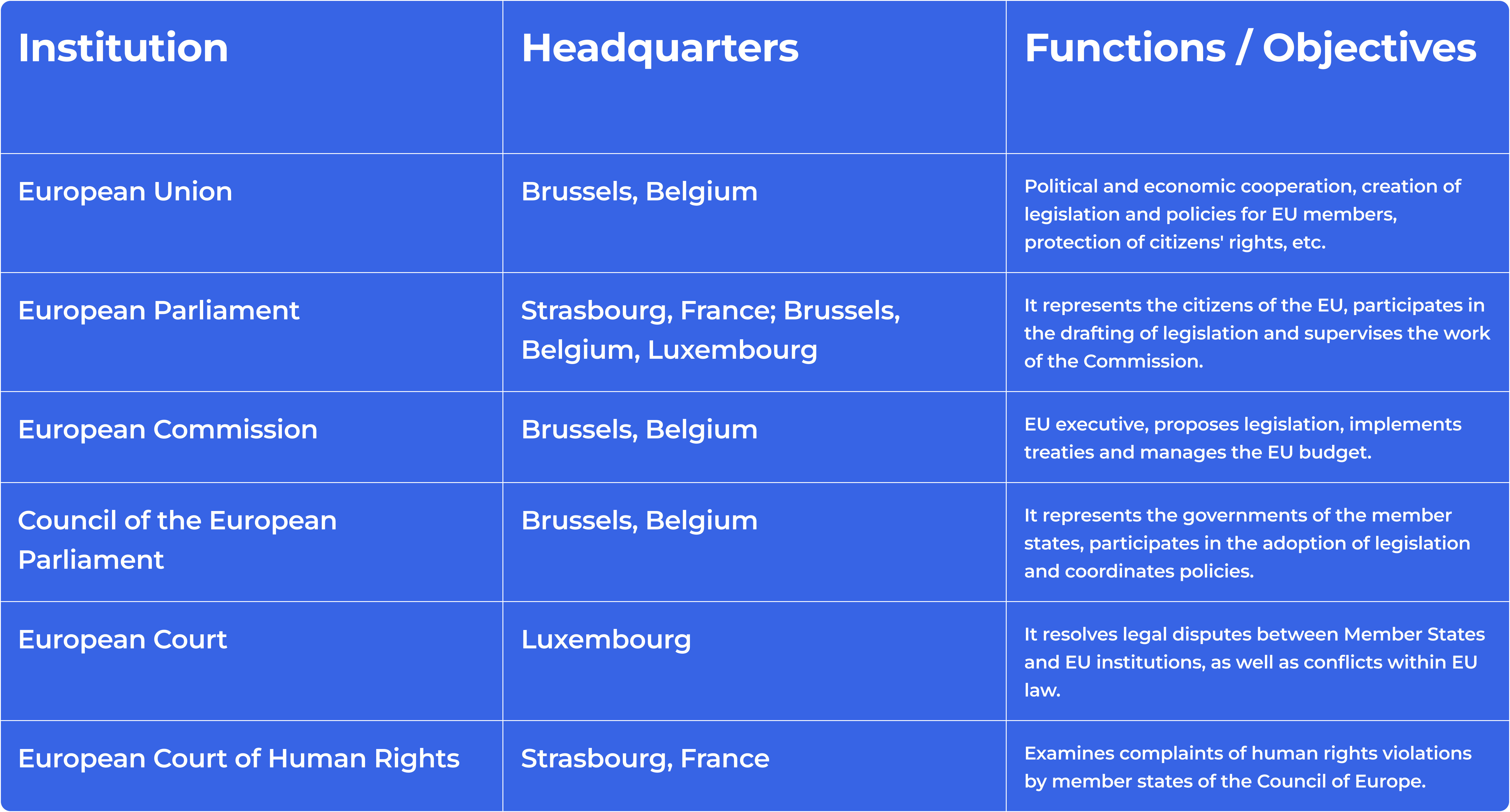

The European Union is an intergovernmental organization made up of 27 European countries that cooperate on issues such as economy, trade, security and environment. It has institutions that manage standard policies and legislation, such as the European Commission, the European Parliament, and the Council of the European Union.
The European Parliament is the only body directly elected by EU citizens and has an essential role in creating legislation and supervising the other institutions. The European Commission is an executive body that proposes new legislation and ensures the implementation of already adopted laws. The Council of the European Union represents the member states and participates in adopting laws.
EU policy covers various areas, such as free movement of people, goods and services, and common currency - the euro. Cooperation in justice and home affairs, standard agricultural policy, environmental policy, and others..
The political challenges that Europe is facing include migration flows, climate change, social and economic inequalities, and relations with global players.

 Community
Community
 Institutions
Institutions
 Information pages
Information pages

 Test
Test







 Civic education lessons
Civic education lessons
 Youth engagement in action
Youth engagement in action
An example of such a program is "Erasmus+ for Youth", which provides opportunities for training, youth exchange, volunteering and partnerships between organizations in different countries. This program supports the youth in acquiring new skills, developing creativity and leadership skills, and understanding Europe's cultural diversity and common values.

 Benefits of youth engagement
Benefits of youth engagement

1.Developing leadership skills:: Participation in youth organizations and projects allows young people to develop leadership skills such as communication, team leadership, leadership, and organization.
2.Acquisition of new knowledge and skills Engaged youth can acquire new knowledge and skills in various fields such as education, technology, social sciences, etc.
3. Increasing self-esteem and confidence: Participation in youth initiatives allows young people to express themselves, share their ideas, and be part of decisions, which can increase their self-esteem and confidence.
4. Support for social integration: Youth engagement can help the social integration of young people, especially those from vulnerable groups.
5. Building community and friendships: Participation in youth initiatives provides an opportunity to build community and establish new friendships, which is important for psychological well-being.
6. Changing Society: Engaged youth can drive social change by addressing and actively working to solve social issues.
7.Support for democratic values: Youth engagement promotes participation in democratic processes and values, such as voting, freedom of expression, and respect for human rights.
 Opportunities for youth engagement
Opportunities for youth engagement
 Media Literacy and Recognizing Fake News
Media Literacy and Recognizing Fake News
1. Check the source: Check if the news comes from an established and reliable media source. You may be facing a scam if the source is unfamiliar or unknown.
2. Fact-checking: Check facts and information from several different and reliable sources before accepting it as true.
3. Careful reading: Read the entire article, not just the title, before sharing information.
4. Critical thinking: Ask yourself questions like What is the purpose of this news? or Are there any hidden interests.
5.Check photos and videos: Check that the photos and videos accompanying the news are correct and up-to-date.



Youth activism includes participation in various initiatives, programs, and activities that aim to support the development and participation of youth in society. This activity can have multiple positive impacts in various areas such as::
 Evaluation methods
Evaluation methods
 Test
Test







 Living, working, traveling in the EU.
Living, working, traveling in the EU.
Education: Europe has many prestigious universities and educational institutions. Young people have the opportunity to receive a quality education in a variety of fields. Programs such as - provide opportunities for student's mobility and exchange, which allow students to spend a certain period in another member state of the European Union., .
Work and Career: Young professionals can find a variety of work and career opportunities in Europe. Professional mobility can be supported through various programs and initiatives that support job search in different countries. In addition, some countries provide special visa regimes for young people who want to work and live there.

Travel and Discovery: Europe is known for its rich culture, history, and diversity. Young people have the opportunity to travel and discover different countries and cities that offer unique and authentic experiences.
Internships and Training Programs: Many organizations and companies offer internships and training programs for young professionals. This can be an excellent way to develop skills and familiarize yourself with the working environment in Europe.
Startups and Entrepreneurship: If you have ideas and ambitions to create your own business, Europe offers a variety of opportunities for startups and entrepreneurship. Many countries provide support and resources for young entrepreneurs.

 What does it mean to be an active European citizen?
What does it mean to be an active European citizen?
1. Participation in elections:: Voting in European elections is an important way to express your opinion and shape the European Union's political future.
2. Supporting public causes: Engaging with social and environmental issues such as combating climate change, protecting human rights, and supporting vulnerable communities.
3. Participation in civic initiatives: Supporting and signing petitions and initiatives that promote changes in legislation or important public issues..
4. Participation in exchange programs and projects: Examples include student exchange programs such as Erasmus+, which support cross-cultural exchange and learning in different countries.


1. Actively monitoring political events: Staying informed about the development of European policy and participating in discussions on important issues.
2. Participation in community organizations: Joining non-governmental organizations and groups working in education, culture, healthcare, and other areas.
3. Utilizing free movement rights: Taking advantage of free travel, work, and learning opportunities in different member states.

 What does the EU do for its citizens?
What does the EU do for its citizens?
1. Freedom of movement and the right to work: The European Union supports the free movement of people, goods, services, and capital within its territory. Citizens of member states have the right to work, study, and live in any other member state without the need for a work visa.
2. Education and science: Programs like Erasmus+ provide educational and student mobility opportunities, allowing students and educators to study and teach in other member states. The EU also supports scientific research and innovation through various programs and financial instruments.
3. Social protection and workers' rights: The EU promotes the implementation of working conditions, equal pay, and social rights standards in all member states. This includes legislation on minimum workers' rights, such as leave, working hours, and a ban on discrimination.

4. Healthcare and food safety: The EU ensures its citizens a high healthcare and food safety standard by regulating the EU's production, labeling, and sale of food and medicines.
5. Consumer protection: The EU has legislation that protects consumer rights and informs them about their rights when purchasing goods and services.
6. Environmental and climate policy: The EU works to preserve the environment and reduce the impact of climate change, creating legislation and programs to promote sustainable practices in various areas.
7. Combating poverty and social exclusion: EU programs and funds are used to support socially vulnerable groups and to combat poverty and social exclusion.

 What are the European Union instruments?
What are the European Union instruments?
1. European Parliament: The body of representative democracy meets in Strasbourg and Brussels. It participates in the legislative process and supervises the activities of other institutions.
2. European Commission: The body responsible for implementing EU legislation and representing the interests of the Union on the global stage.
3. Council of the European Union: A forum for coordinating the policies of member states and making decisions in important areas.
4. Council of Ministers: Members of this council are ministers from the governments of member states who discuss specific issues according to their thematic area, such as the economy, foreign relations, etc.
5. European Council: Includes the heads of state or government of member states and the President of the European Commission. This body establishes common guidelines and development strategies for the European Union.
6. European Central Bank: Responsible for managing the euro and monetary policy in the eurozone.
7. European Investment Bank: Supports projects focused on infrastructure, economic development, and innovation in the European Union.
8. European Investment Service: Provides financial and technical resources for project implementation in various fields.
9. European External Action Service: Coordinates the EU's foreign policy and represents the Union internationally.
10. European Environment Agency, European Medicines Agency, and others: Specialized agencies that support regulatory and scientific aspects in specific areas.
 Documents and Publications Following the Priorities of the 'Erasmus+' Program.
Documents and Publications Following the Priorities of the 'Erasmus+' Program.
1. Youth Plan (2019-2027): This is a strategic document of the EU that outlines priorities and actions to support youth in Europe. It includes various measures to improve education, employment, participation, and youth mobility.
2. Erasmus+ Portal: The official website of the 'Erasmus+' program contains information on all aspects of the program, including opportunities for young people. You can find information about educational programs, scholarships, exchange programs, and other mobility opportunities here.
3. European Youth Strategy (2010-2018): This document presents a strategy for integrating young people into education, employment, participation, and culture. It also provides useful guidelines for understanding the youth sector in the European Union.

4. EU Reports and Analyses on Youth Policy: The European Commission and other EU bodies regularly publish reports, analyses, and statistical data on various aspects of youth policy and employment.
5. EU Directives and Legislation: The official website of the 'Erasmus+' program contains information on all aspects of the program, including opportunities for young people. You can find information about educational programs, scholarships, exchange programs, and other mobility opportunities here.
6. Seminars, Events, and Training in the Youth Sector: This document presents a strategy for integrating young people into education, employment, participation, and culture. It also provides useful guidelines for understanding the youth sector in the European Union.
With these resources, you'll be able to familiarize yourself with the priorities of the 'Erasmus+' program and the youth sector of the EU, as well as the opportunities provided to young people.


 Test
Test

